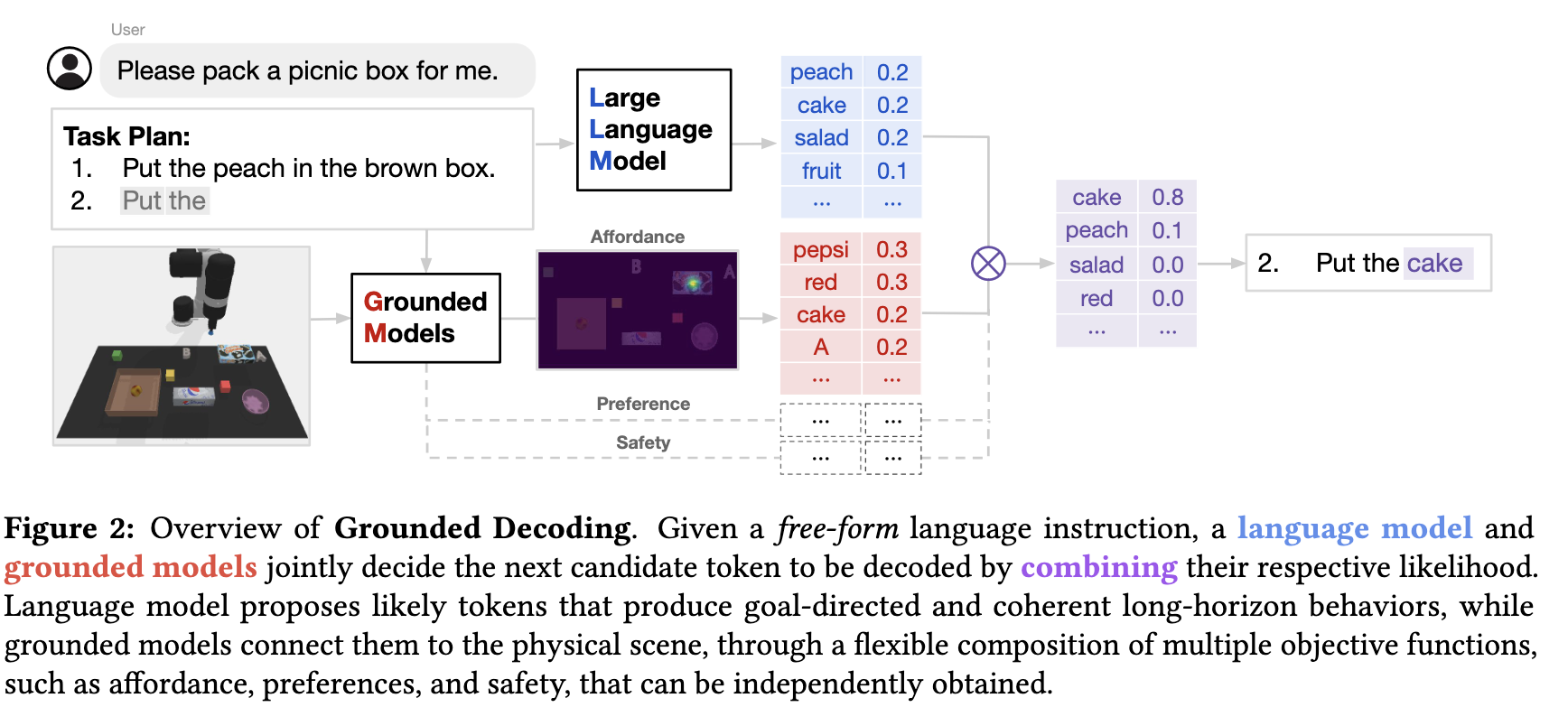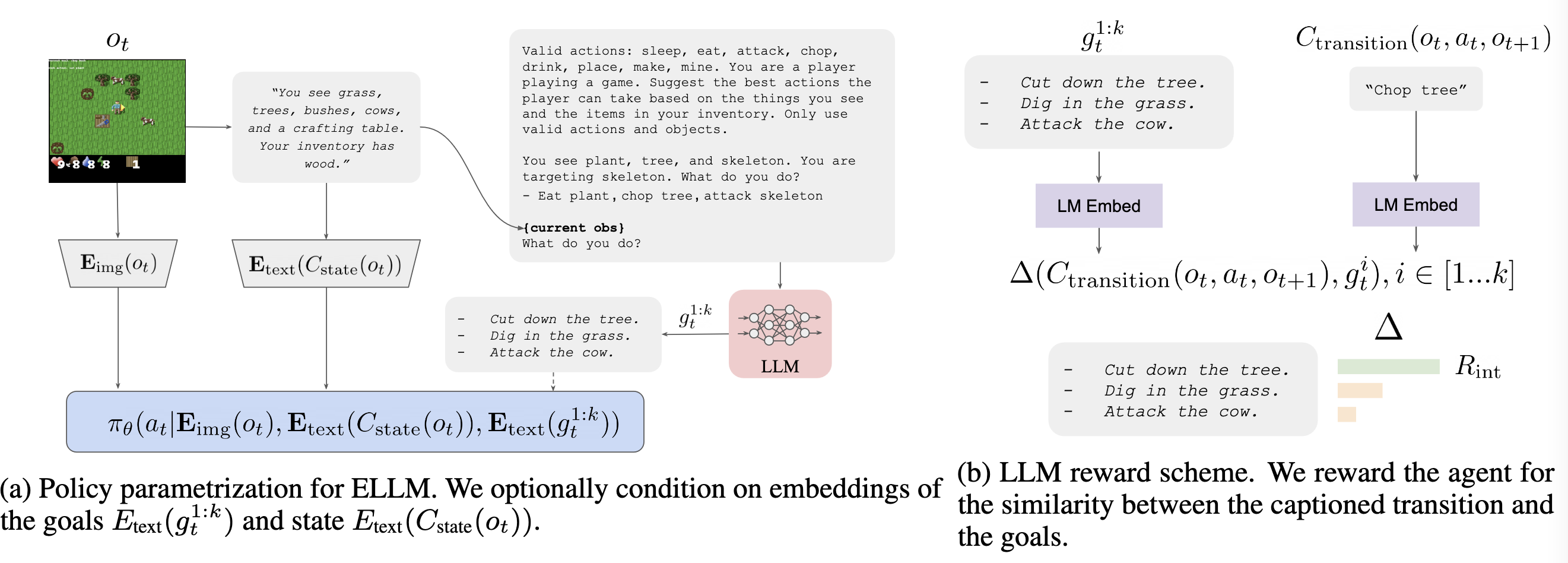
Jacob_andreas Guiding Pretraining in Reinforcement Learning With Llms 2023
[TOC] Title: Guiding Pretraining in Reinforcement Learning With Large Language Models Author: Yuqing De, Jacob Andreas et. al. Publish Year: 13 Feb 2023 Review Date: Wed, Apr 5, 2023 url: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.06692.pdf Summary of paper Motivation intrinstically motivated exploration methods address sparse reward problem by rewarding agents for visiting novel states or transitions. Contribution we describe a method that uses background knowledge from text corpora to shape exploration. This method, call Exploring with LLMs, reward an agent for achieving goals suggested by a language model prompted with a description of agent’s current state. Some key terms How does ELLM work ...