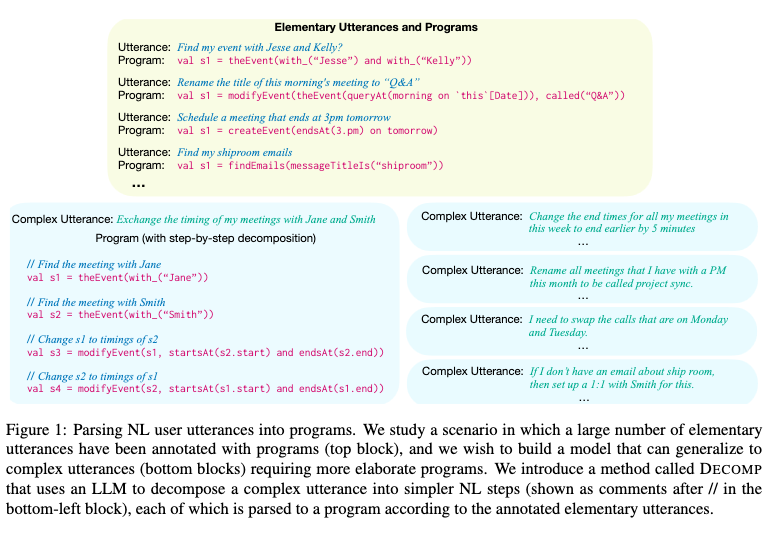
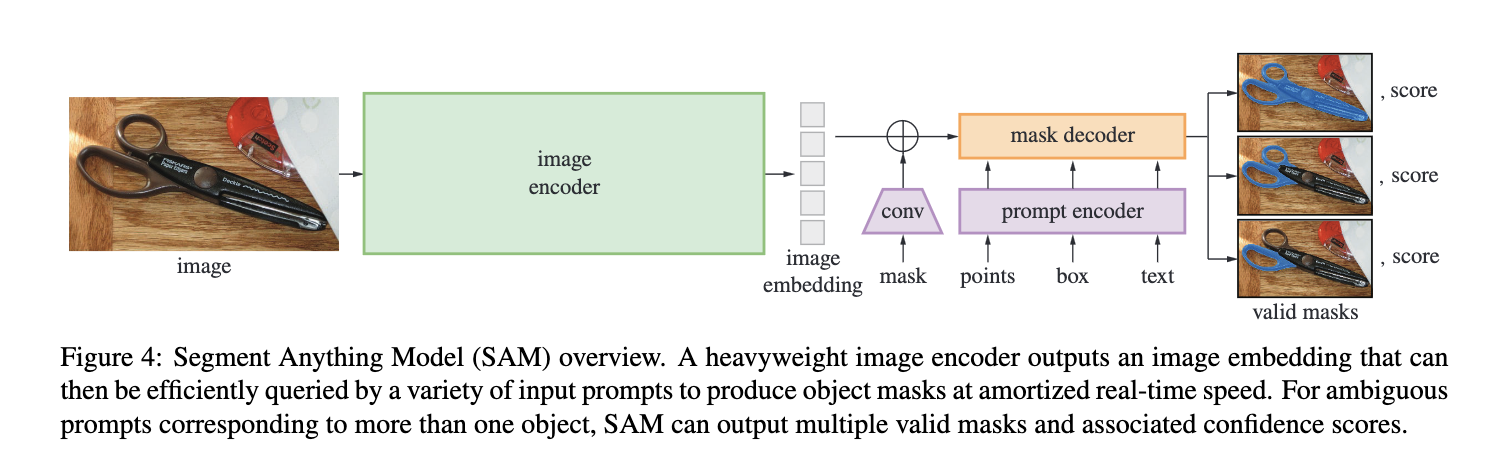
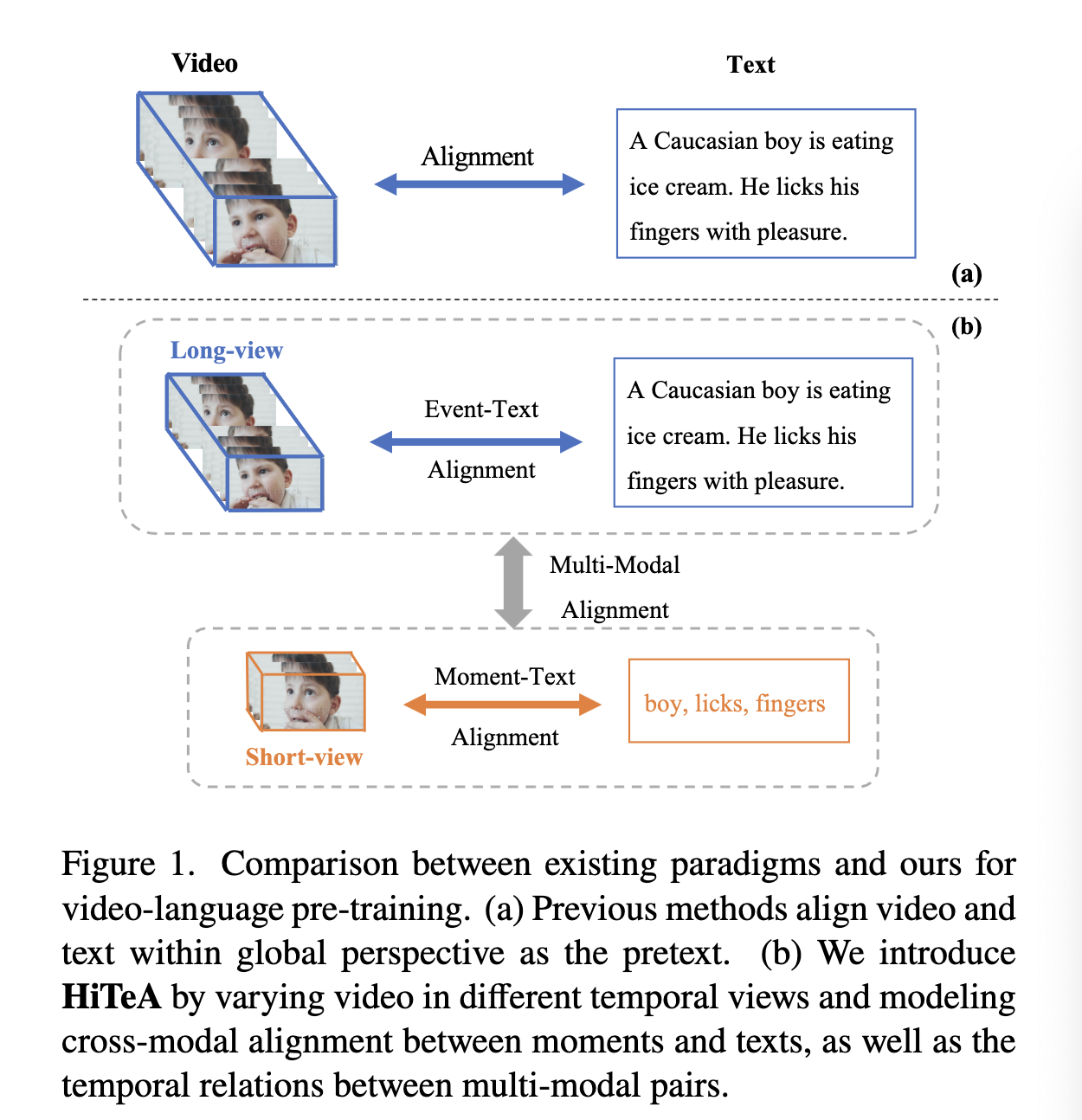
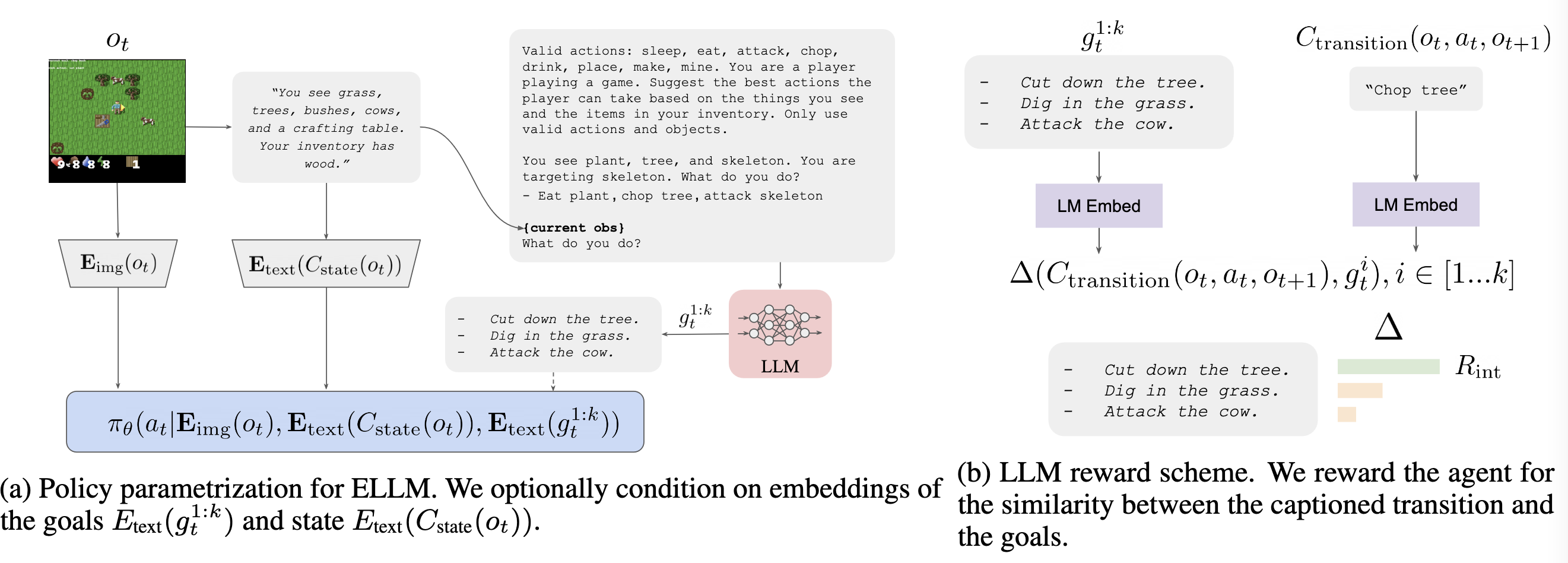
[TOC]
Title: How Robust Is GPT 3.5 to Predecessors a Comprehensive Study on Language Understanding Tasks Author: Xuanting Chen et. al. Publish Year: 2023 Review Date: Mon, Apr 3, 2023 url: https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2303/2303.00293.pdf Summary of paper Motivation GPT3.5, their robustness, and abilities to handle various complexities of the open world have yet to be explored, which is especially crucial in assessing the stability of models and is a key aspect of trustworthy AI Contribution Our study yielded the following findings by comparing GPT 3.5 with finetuned models competitive results on test sets: GPT3.5 achieves SOTA results in some NLU tasks compared to supervised models fine-tuned with task-specific data. In particular GPT-3.5 performs well in reading comprehension and sentiment analysis tasks, but face challenges in sequence tagging and relation extraction tasks. Lack of robustness: GPT-3.5 still encounter significant robustness degradation, such as its average performance dropping by up to 35.74% and 43.59% in natural language inference and sentiment analysis tasks, respectively. However, it is worth noting that GPT3.5 achieves remarkable robustness on certain tasks, such as reading comprehension and WSC tasks Robustness instability: In few-shot scenarios, GPT-3.5’s robustness improvement varies greatly across different tasks. For example, GPT-3.5 shows significant improvement in aspect-based sentiment analysis tasks while the robustness actually decreases in natural language inference (Section 4.3.1) and semantic matching (Section 4.3.2) tasks. Prompt sensitivity: changes in input prompts have a significant impact on the results, and GPT-3.5’s robustness to prompt variations. still requires improvement. Number sensitivity: GPT3.5 is more sensitive to numerical inputs than pre-training fine-tuning models. For example, in the NumWord transformation, which involves replacing numerical words in sentences with different numerical values, GPT3.5 exhibits a significantly high level of sensitivity. Task labels sensitivity: we speculate that the task construction during the instruction tuning stage may significantly impact the model’s performance. In the case of IMDB binary sentiment classification dataset, the model outputs a large number of “neutral” responses, which are not included in the application label space, resulting in a performance drop Significant improvement in zero/few-shot scenarios: in zero-shot and few-shot scenario, GPT3.5 outperforms existing LLMs in most NLU tasks, especially in reading comprehension, natural language inference and semantic matching tasks Ability for in-context learning: Compared to 0-shot, GPT 3.5 performs better on most tasks in the 1-shot setting. Additionally, performance does no vary significantly between the 1-shot, 3-shot, 6-shot, 9-shot settings for most tasks. However, providing additional examples in the prompts can be advantageous for sequence tagging tasks