Jun Wang Conformal Temporal Logic Planning Using Llm 2023
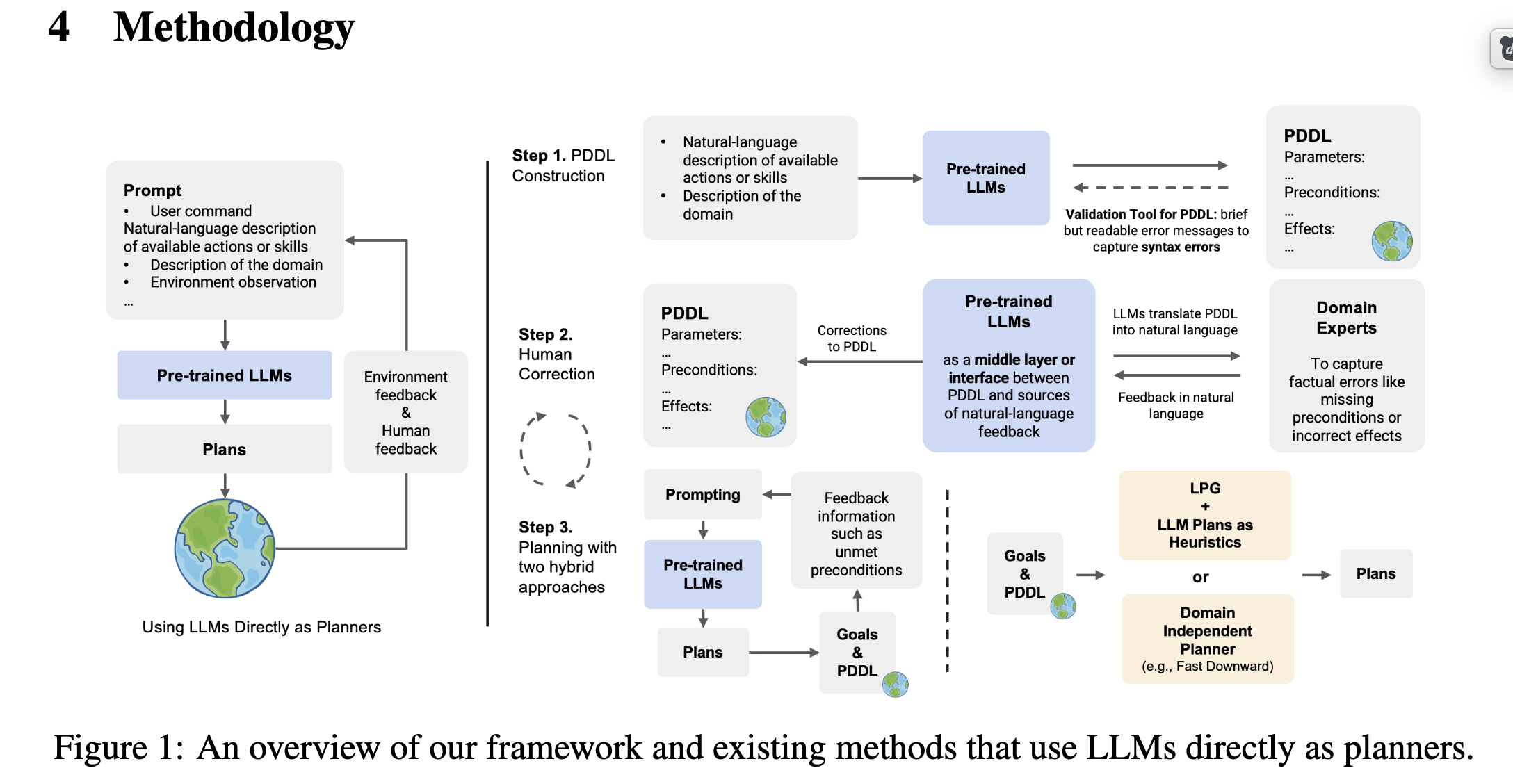
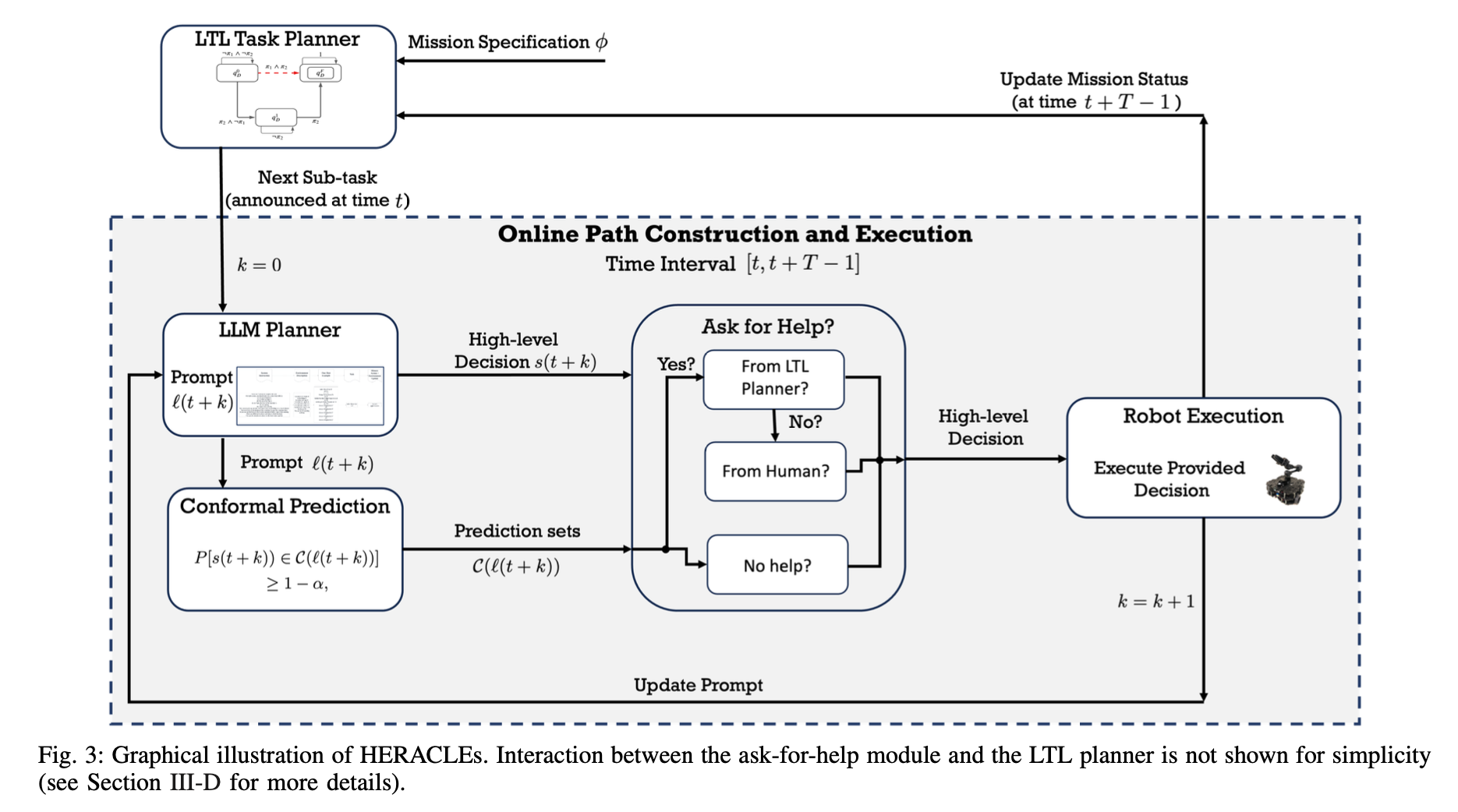
[TOC] Title: Conformal Temporal Logic Planning Using Llm 2023 Author: Jun Wang et. al. Publish Year: 19 Dec, 2023 Review Date: Sun, Jan 21, 2024 url: arXiv:2309.10092v2 Summary of paper Motivation Unlike previous methods that focus on low-level system configurations, this approach focuses on NL-based atomic propositions. now the LTL tasks are defined over NL-based atomic propositions Robots are required to perform high-level sub tasks specified in natural language. To formally define the overarching mission, they leverage LTL defined over atomic predicates modelling these NL-based sub-tasks. Contribution To address the challenge of ensuring the correctness of robot plans with respect to these LTL-encoded tasks, the authors propose HERACLEs, a hierarchical conformal natural language planner. HERACLEs employs automata theory to determine the next NL-specified sub-tasks for mission progress, employs Large Language Models to design robot plans to fulfill these sub-tasks, and uses conformal prediction to assess the probabilistic correctness of the plans, deciding whether external assistance is needed. The paper provides theoretical probabilistic guarantees for mission satisfaction and presents extensive comparative experiments on mobile manipulation tasks. Some key terms Limitation for previous work ...