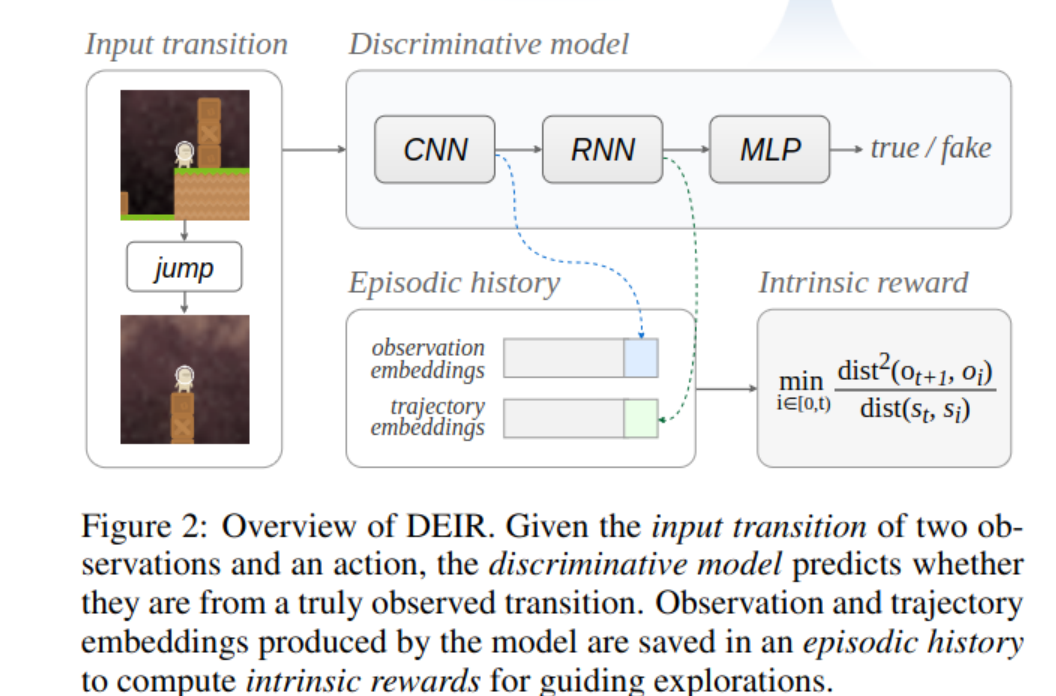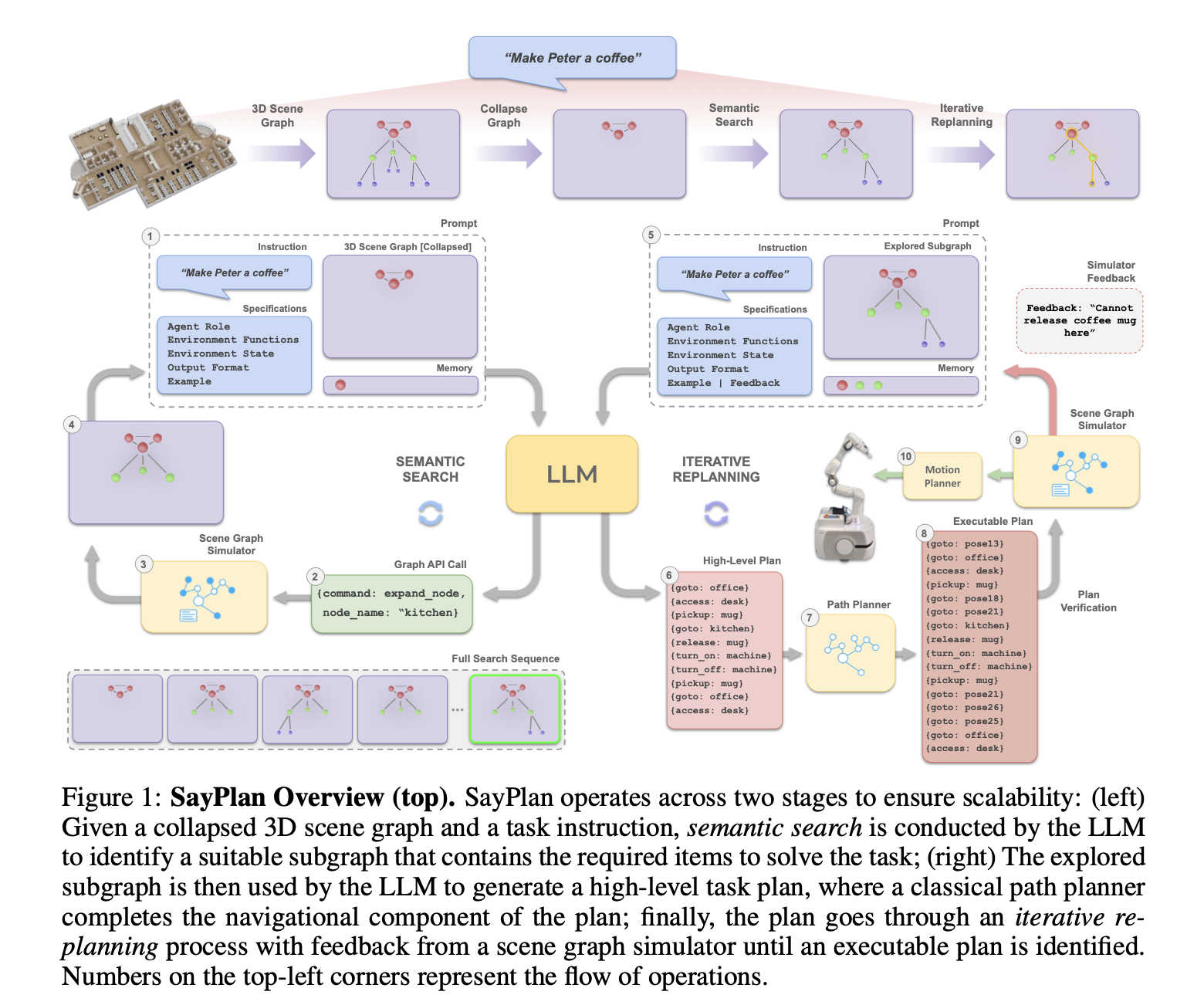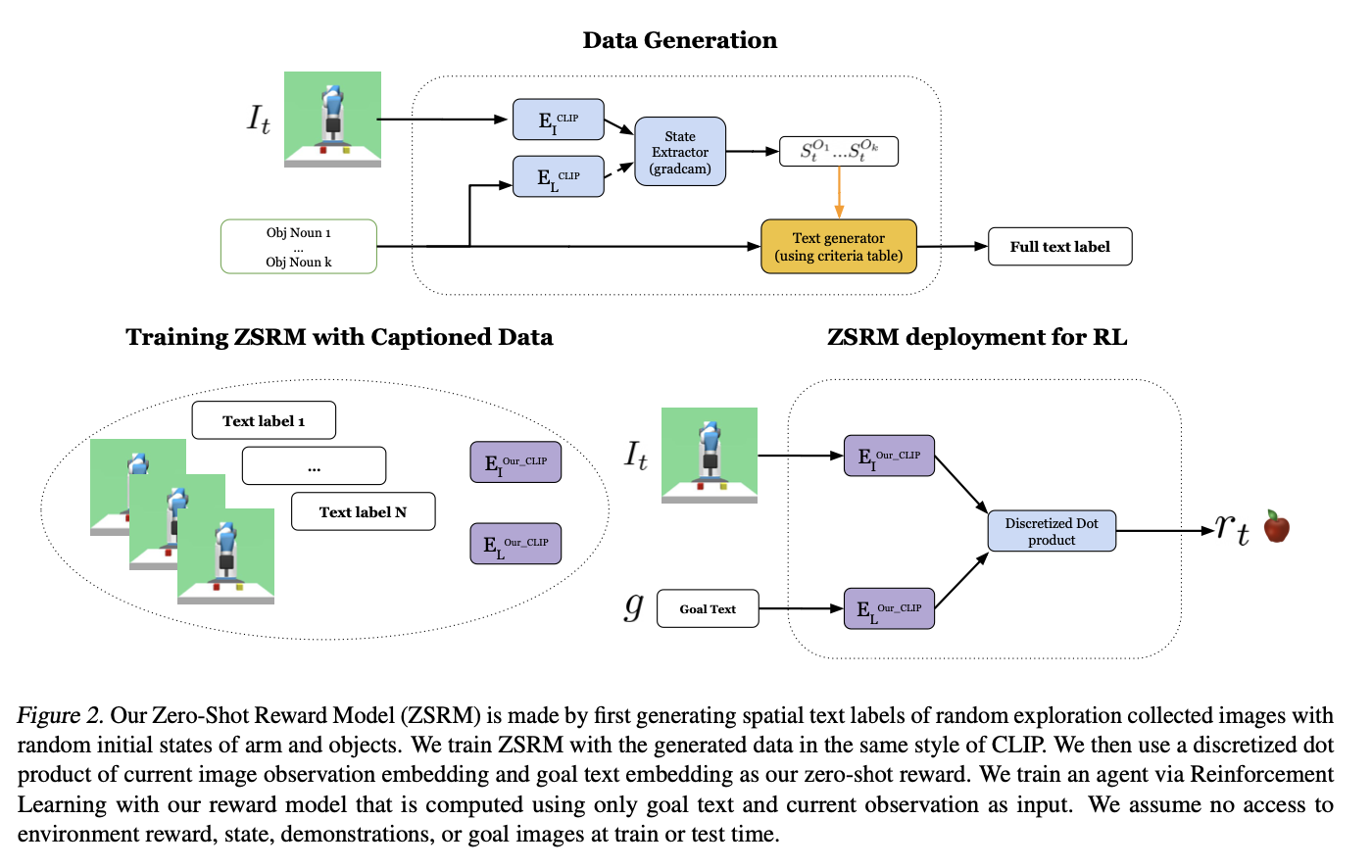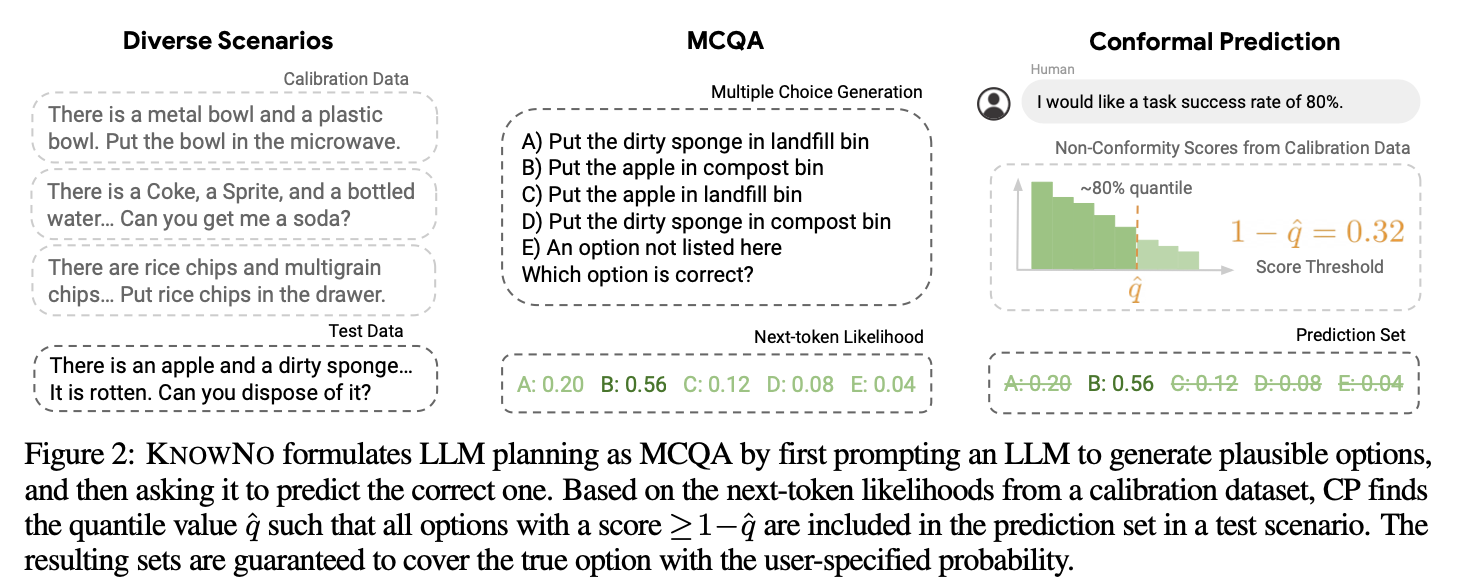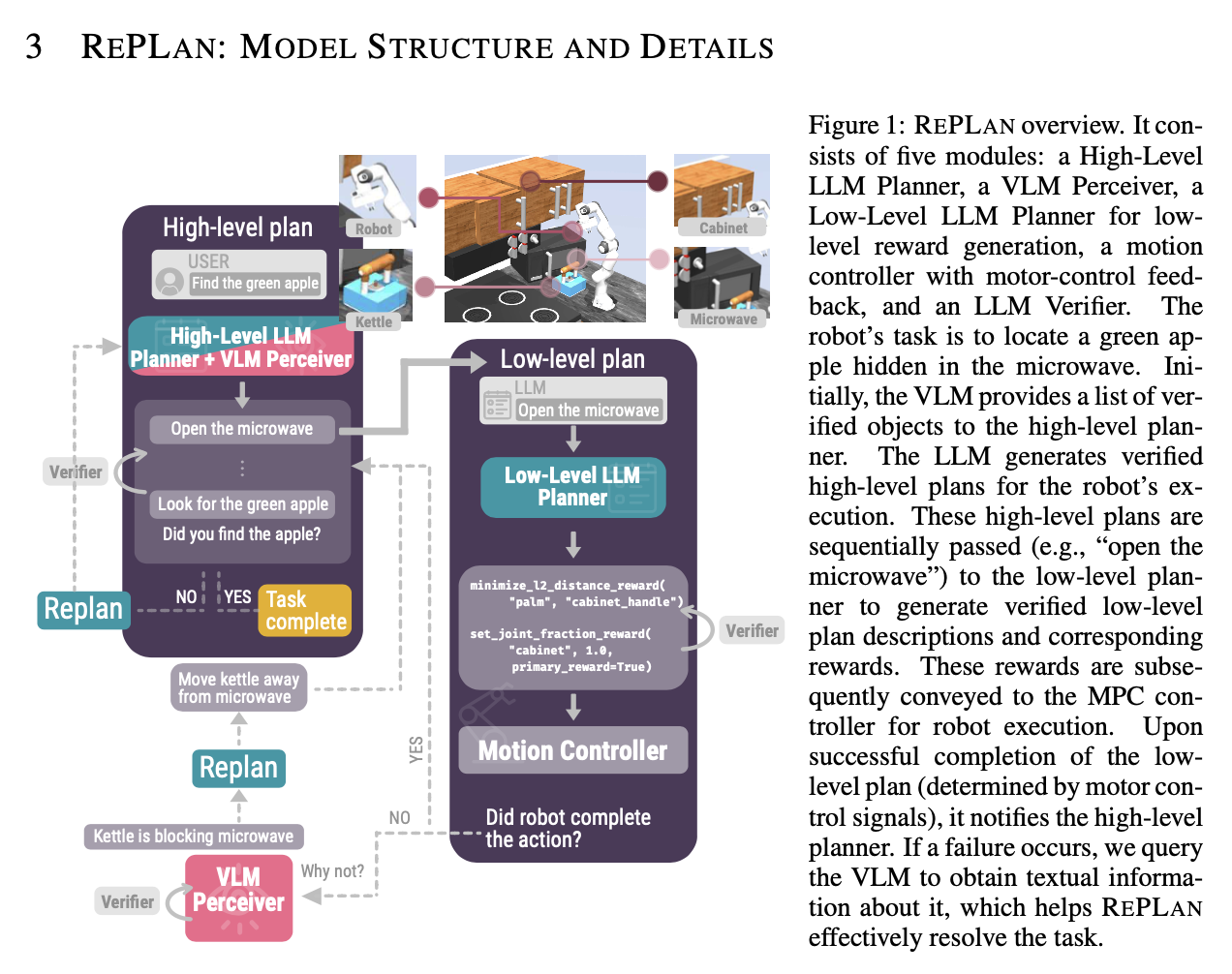
Daniel Hierarchies of Reward Machines 2023
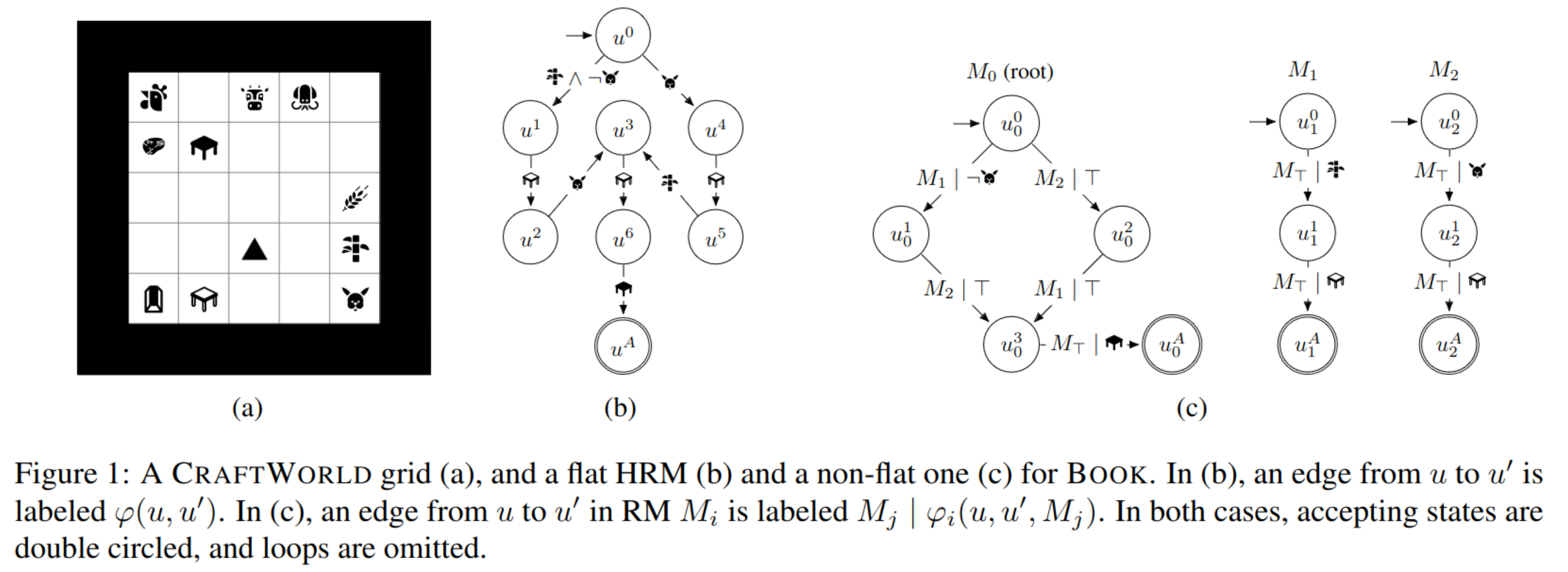
[TOC] Title: Hierarchies of Reward Machines Author: Daniel Furelos-Blanco et. al. Publish Year: 4 Jun 2023 Review Date: Fri, Apr 12, 2024 url: https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.15752 Summary of paper Motivation Finite state machine are a simple yet powerful formalism for abstractly representing temporal tasks in a structured manner. Contribution The work introduces Hierarchies of Reinforcement Models (HRMs) to enhance the abstraction power of existing models. Key contributions include: HRM Abstraction Power: HRMs allow for the creation of hierarchies of Reinforcement Models (RMs), enabling constituent RMs to call other RMs. It’s proven that any HRM can be converted into an equivalent flat HRM with identical behavior. However, the equivalent flat HRM can have significantly more states and edges, especially under specific conditions. ...